Particle Size Analyzer Equipment Manual (Mastersizer 2000)
Today, we introduce the methods for using and interpreting reports from the
Mastersizer2000 particle size analyzer from Malvern, which is widely used by many for research and experiments in particle size analysis.
If you need any related files mentioned below, please send an email to info.korea@malvern.com or leave a comment ![]()

1. Overview
1) The MS2000 is designed to measure the mean particle size and distribution of particles suspended in a dispersant (powder/liquid).
2) It measures using the laser diffraction method with Mie theory (ISO 13320-1).
3) Measures the diameter of a sphere with the same volume as the test material, regardless of particle shape.
4) Two types of dispersion (Wet, Dry) can be measured.
5) Select dispersion unit based on capacity/purpose, automatic status.
– Wet: Hydro 2000 (G, S, MU, SM, uP) – Dry: Scirocco 2000
6) Specification (Optical bench)
– Size range(2000): 0.02 ~ 2,000 um (varies by sample properties) (2000E): 0.1 ~ 1,000 um (varies by sample properties) – Light sources: Red (He-Ne laser: 633 nm) Blue (Solid state light source: 466 nm) – MS 2000 only
7) Typical systems
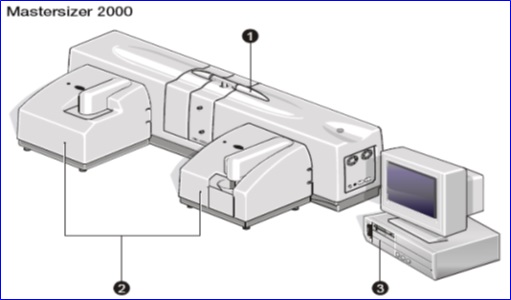
① Optical bench ② One or more sample dispersion units (both wet and dry usable) ③ Computer system
2. Interpretation and Understanding of Analysis Data
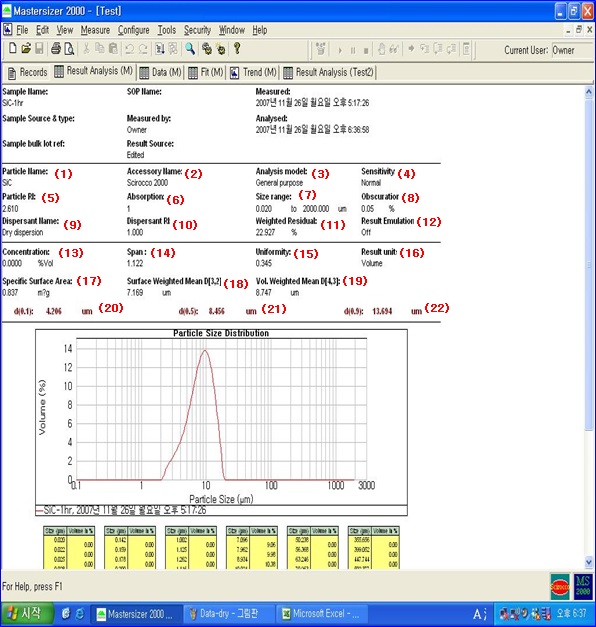
(1) Particle Name: Name of the sample (2) Accessory Name: Name of dispersion unit (e.g., Scirocco 2000, Hydro S, …) (3) Analysis models: Calculation mode (e.g., General purpose, Multiple narrow modes…) (4) Sensitivity: Calculation sensitivity (e.g., Normal, Enhanced) (5) Particle RI: Refractive index of sample (e.g., 1.52(default), 1.65, 1.75, …) (6) Absorption: Absorptivity of sample (e.g., 1, 0.1, 0.01, …) (7) Size range: Size range of measured result (e.g., 0.020 to 2000.000um) (8) Obscuration: Degree to which the sample shields the laser (proportional to sample concentration) Wet: 5~20% (adjustable based on sample), Dry: 0.6~5% (9) Dispersant Name: Type of dispersant (e.g., Dry dispersion, Water, …) (10) Dispersant RI: Refractive index of dispersant (e.g., 1.33 (water), 1.00 (Dry dispersion), …) (11) Weighted Residual: Indicates how well calculated results match the measured data 2% or less: Good, more than 2%: Indicates incorrect refractive index or absorptivity of sample, or dispersant’s refractive index. (12) Result Emulation: Modify results with other particle size measurement methods (13) Concentration: Volume concentration % of solid sample (calculated using Beer-Lambert law) (14) Span: Distribution width (smaller value indicates narrower distribution) Span = [ D (v, 0.9) – D (v, 0.1) ] / D (v, 0.5) (15) Uniformity: Absolute deviation from D(v,0.5) (16) Result units: Measurement units (e.g., Volume, Surface, …) (17) Specific Surface Area (SSA): Specific surface area (total surface area divided by total volume) SSA = 6 / p D [ 3 , 2 ] (where, p: particle density) Calculated assuming particles are spherical without pores (m2/g) (18) Surface Weighted Mean D[3,2]: Surface mean, Sauter Mean (19) Volume Weighted Mean D[4,3]: Volume mean (20) d(0.1): Size at 10% of total particle size distribution (21) d(0.5): Size at 50% of total particle size distribution, Median (22) d(0.9): Size at 90% of total particle size distribution
This article may have been translated automatically
{{ product.product_name }}
{{ product.product_strapline }}
{{ product.product_lede }}
