氫催化劑分析
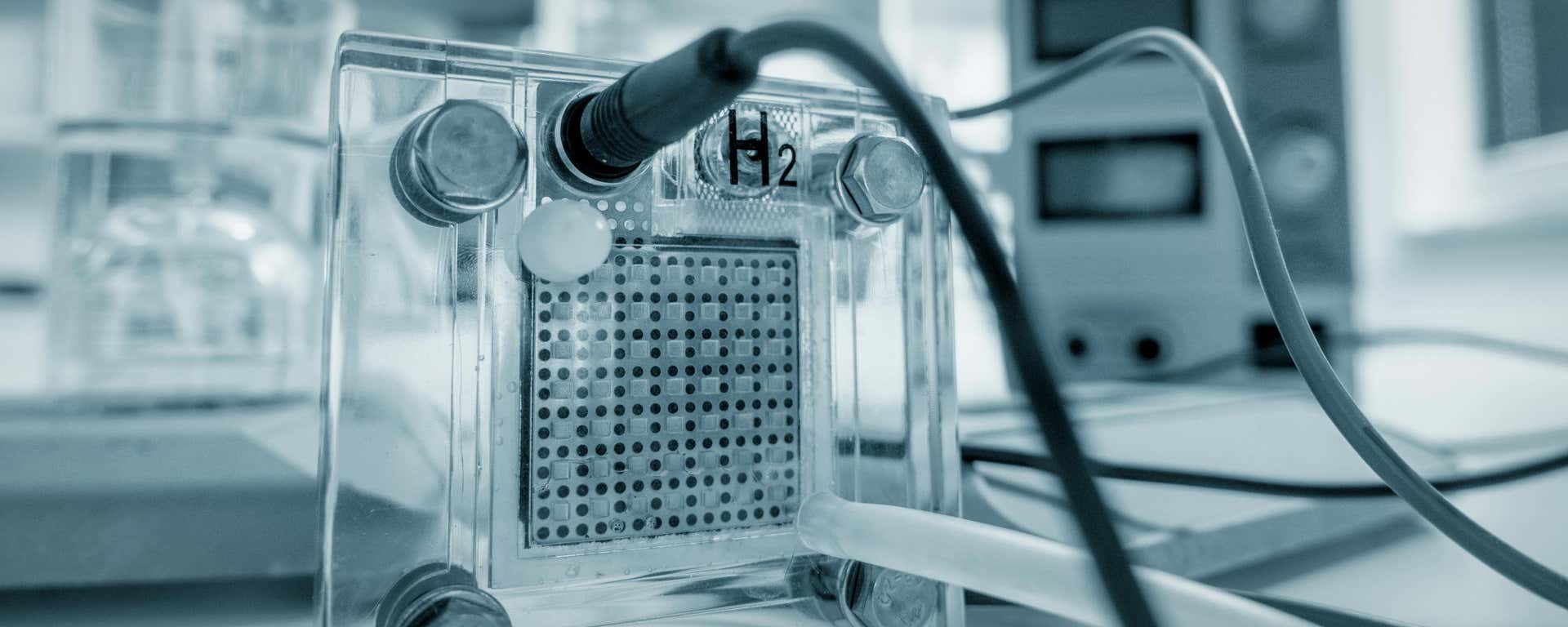

氫可以成為潔淨能源載體,減少各類領域對化石燃料的依賴,並為脫碳提供強大助力:
氫氣支援超過 60% 的高 GHG 排放應用,且其全球碳減量占比預計將於 2050 年前達到 20%,對於淨零碳排放的未來至關重要。
氫催化劑對於提高氫氣生產、儲存與使用的效率方面至關重要。它們的功用遍及多項技術:
氫經濟的關鍵要素包括:
技術:
材料:吸附劑、薄膜、催化劑
測量目標:
技術
氫氣可用以下形式儲存:
材料:吸附劑、催化劑
測量目標:
技術
氫氣具有多種用途:
材料:薄膜、催化劑、吸附劑
測量目標:

體積小但功能強大的攜帶式 XRF 分析儀

高效能氣體吸附
