Overview
The PEAQ-ITC Automated, a MicroCal technology, combines the high sensitivity of the PEAQ-ITC - the calorimeter core of the system - with walkaway automation, to meet the productivity needs of busy research and drug discovery laboratories.
The system directly measures heat released or absorbed during biochemical binding events, from which it calculates binding affinity (KD), stoichiometry (n), enthalpy (ΔH), and entropy (ΔS).
Other than preparing samples and reagents to appropriate concentrations, there is minimal assay development, and time to first result is fast. Easy-to-use software includes optimized automation scripts for robust operation with a variety of sample types and conditions.

Features and benefits
- User-friendly design tools assist in selecting experimental run parameters
- All binding parameters (affinity, stoichiometry, enthalpy and entropy) in a single experiment
- Quick to first result with minimal assay development, no labelling, no immobilization and no molecular weight limitations
- High signal-to-noise gives more confidence in assessing data quality and relevance of generated affinity and thermodynamic parameters
- Outstanding data quality for sub-millimolar to picomolar dissociation constants (10-2 to 10-12 M)
- Coin-shaped cell optimizes sample mixing
- Nonreactive Hastelloy for chemical resistance and compatibility with biological samples
- Sensitivity to investigate any biomolecular interaction using as little as 10 µg of protein
- Samples presented in a temperature-controlled 96-well plate
- Fully automated system with walk-away operation for enhanced productivity

How it works
Isothermal titration microcalorimeters measure the heat change that occurs when two molecules interact. Heat is released or absorbed as a result of the redistribution and formation of non-covalent bonds when the interacting molecules go from the free to the bound state.
ITC monitors these heat changes by measuring the differential power, applied to the cell heaters, required to maintain zero temperature difference between the reference and sample cells as the binding partners are mixed.
The reference cell usually contains water, while the sample cell contains one of the binding partners (the sample, often but not necessarily a macromolecule) and a stirring syringe which holds the other binding partner (the ligand).
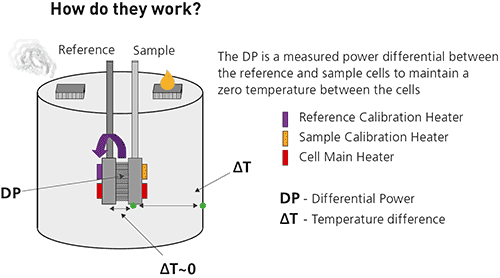
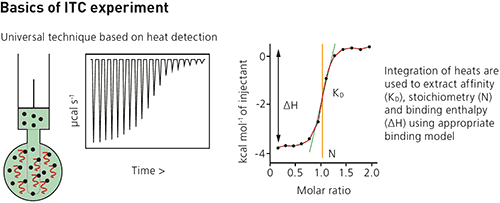
The ligand is injected into the sample cell, typically in 0.5 to 2 μL aliquots, until the ligand concentration is two- to three-fold greater than the sample.
Each injection of ligand results in a heat pulse that is integrated with respect to time and normalized for concentration to generate a titration curve of kcal/mol vs molar ratio (ligand/sample).
The resulting isotherm is fitted to a binding model to generate the affinity (KD ), stoichiometry (n) and enthalpy of interaction (ΔH).
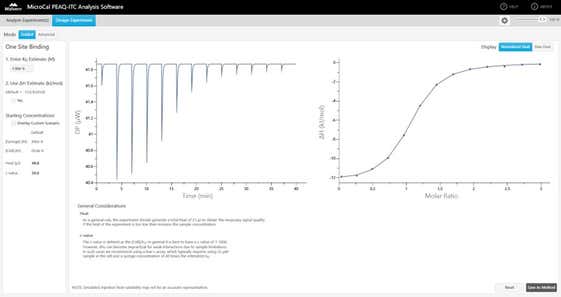
Analysis software
Core PEAQ-ITC Analysis software offers experiment design simulation, batch evaluation of large data sets, automated assessment of data quality and a streamlined user interface that guides the user to final figures and presentation quality graphs quickly and easily.
- Open multiple experiments in a single session
- Supports many automated fitting models
- Dissociation
- Enzyme Kinetics - Multiple Injections
- Enzyme Kinetics - Single Injection
- One Set of Sites
- Sequential Binding Sites
- One Set of Sites - SIM
- Two Sets of Sites
- Competitive
- Automated assessment of data quality
- Good quality data - Binding
- Good quality data - No binding
- Poor quality data - Check data
Very good instrument, fast and easy to use."
Clarissa Melo Czekster — University of St Andrews








![[PN13012_2520_CLV_Photography_MP_JN.jpg] PN13012_2520_CLV_Photography_MP_JN.jpg](https://dam.malvernpanalytical.com/1b3bd0b0-1f31-43bf-a862-ae5100d0f47e/PN13012_2520_CLV_Photography_MP_JN_Original%20file.jpg)
