水素触媒分析
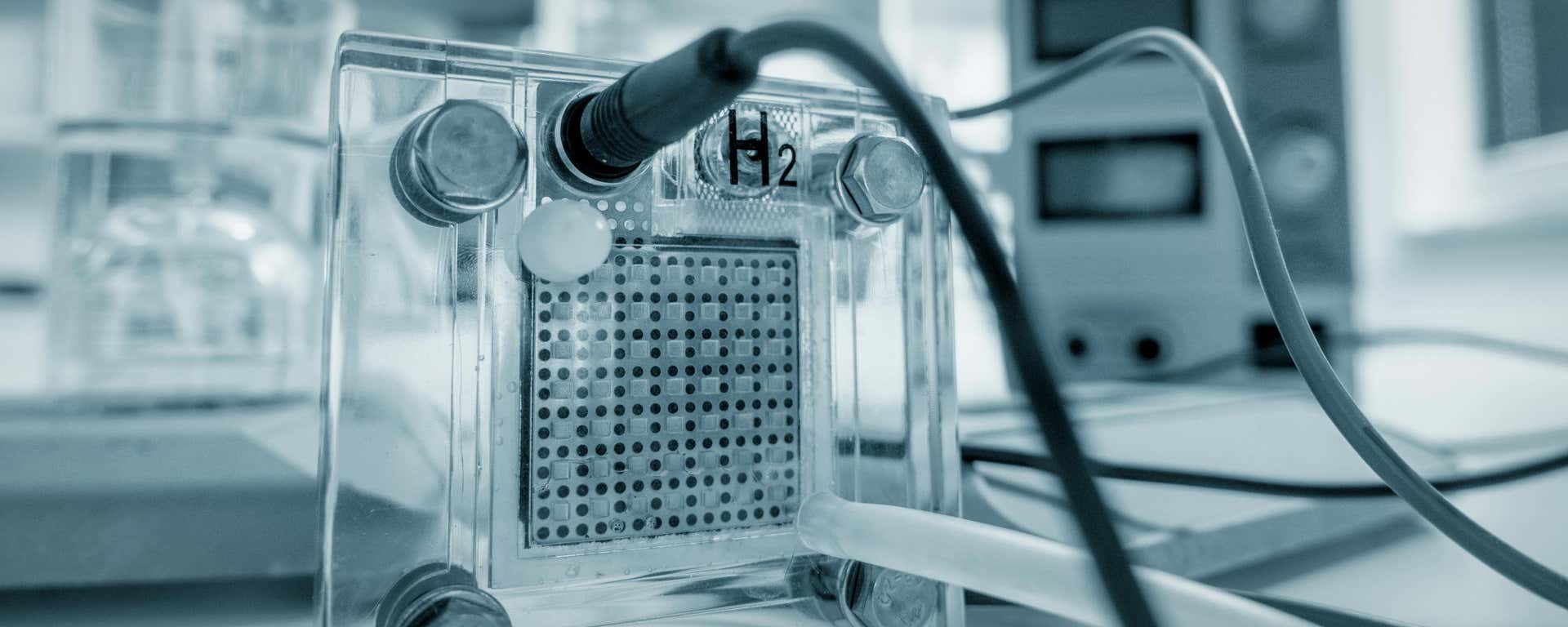

水素はクリーンエネルギーの担体として機能し、化石燃料への依存を減らすことにより、さまざまな分野の脱炭素化に大きく貢献できます。
水素は温室効果ガス高排出用途の60%以上を支え、2050年までに世界の炭素削減の20%以上に貢献すると予測されており、ネットゼロの未来に不可欠なものとなっています。
水素触媒は、水素の生産、貯蔵、利用効率を高めるために重要です。水素触媒の役割は、複数の技術にまたがります。
水素ベースの経済の主要な構成要素は次のとおりです。
技術:
材質:吸着剤、膜、触媒
測定目標:
技術
水素を次の方法で貯蔵可能:
材質: 吸着剤、触媒
測定目標:
技術
水素は汎用性が高い:
材質: 膜、触媒、吸着剤
測定目標:

たった40×40cmのスペースで元素分析 小型・パワフルな卓上XRF

高性能ガス吸着測定装置
